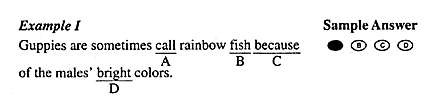The following is a test sample of Section 3 Reading Comprehension.
Now begin work on the questions.
PRACTICE PASSAGE
The
Alaska pipeline starts at the frozen edge of the Arctic Ocean.
It
stretches southward across the largest and northernmost state in
the
United States, ending at a remote ice-free seaport village nearly
Line 800
miles from where it begins. It is massive in size and extremely
(5) complicated
to operate.
The
steel pipe crosses windswept plains and endless miles of
delicate
tundra that tops the frozen ground. It weaves through
crooked
canyons, climbs sheer mountains, plunges over rocky
crags,
makes its way through thick forests, and passes over or
(10) under
hundreds of rivers and streams. The pipe is 4 feet in diameter,
and
up to 2 million barrels (or 84 million gallons) of crude oil can
be
pumped through it daily.
Resting
on H-shaped steel racks called "bents," long sections of
the
pipeline follow a zigzag course high above the frozen earth.
(15) Other
long sections drop out of sight beneath spongy or rocky
ground
and return to the surface later on. The pattern of the
pipeline's
up-and-down route is determined by the often harsh
demands
of the arctic and subarctic climate, the tortuous lay of the
land,
and the varied compositions of soil, rock, or permafrost
(20) (permanently
frozen ground). A little more than half of the pipeline
is
elevated above the ground. The remainder is buried anywhere
from
3 to 12 feet, depending largely upon the type of terrain and
the
properties of the soil.
One
of the largest in the world, the pipeline cost approximately
(25) $8
billion and is by far the biggest and most expensive construction
project
ever undertaken by private industry. In fact, no single
business
could raise that much money, so 8 major oil companies
formed
a consortium in order to share the costs. Each company
controlled
oil rights to particular shares of land in the oil fields and
(30) paid
into the pipeline-construction fund according to the size of its
holdings.
Today, despite enormous problems of climate, supply
shortages,
equipment breakdowns, labor disagreements, treacherous
terrain,
a certain amount of mismanagement, and even theft, the
Alaska
pipeline has been completed and is operating.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1. The
passage primarily discusses the pipeline's
A. operating
costs
B. employees
C. consumers
D. construction
2. The
word "it" in line 4 refers to
A. pipeline
B. ocean
C. state
D. village
3. According
to the passage, 84 million gallons of oil can travel through the pipeline each
A. day
B. week
C. month
D. year
4. The
phrase "Resting on" in line 13 is closest in meaning to
A. Consisting
of
B. Supported
by
C. Passing
under
D. Protected
with
5. The
author mentions all of the following as important in determining the pipeline's
route EXCEPT the
A. climate
B. lay
of the land itself
C. local
vegetation
D. kind
of soil and rock
6. The
word "undertaken" in line 26 is closest in meaning to
A. removed
B. selected
C. transported
D. attempted
7. How
many companies shared the costs of constructing the pipeline?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 8
D. 12
8. The
word "particular" in line 29 is closest in meaning to
A. peculiar
B. specific
C. exceptional
D. equal
9. Which
of the following determined what percentage of the construction costs each
member of the consortium would pay?
A. How
much oil field land each company owned
B. How
long each company had owned land in the oil fields
C. How
many people worked for each company
D. How
many oil wells were located on the company's land
10. Where
in the passage does the author provide a term for an earth covering that always
remains frozen?
A. Line
3
B. Line
13
C. Line
19
D. Line
32
Answer Key for Reading Comprehension
Section 3 — Reading Comprehension
1. D
2. A
3. A
4. B
5. C
6. D
7. C
8. B
9. A
10. C
For those who want to take a private English course in Bogor, you may contact independent.ec@gmail.com.